1000+
customers

50+ countries
across the world

Outsourcing leader
since 2008

Technology-driven
services

Stringent
quality processes
A Comprehensive Guide to RPA Implementation in Financial Reporting
Last updated: 25 Jan, 2024 By Ashish Rana | 6 Minutes Read
Have you ever imagined what would happen if robots could handle your journal entries, reconciliation processes, and financial reporting? If not, this is the time to know all about RPA in finance and accounting and its effectiveness in financial reporting. Robotic process automation is performing at its best in most business industries, and in to the finance and accounting industry, it is no less than a boon.“Although only 29% of corporate controllers are using it for financial reporting processes, Gartner predicts that by 2020, 88% will use RPA.”
Financial reporting is a vital function for any company, but preparing and submitting such reports requires a skilled and experienced workforce. However, these days, RPA-powered software can do the reporting work accurately in less time. This allows your finance and/or accounting team to get more time to focus on improving your company’s financial performance.
How Does RPA in Finance & Accounting Add Value to your Business?
Do you want to get the most out of implementing automation in your financial reporting services or any other task? To use it to your advantage, you may want to start with:
- Financial close: It collects data from multiple sources and posts it to sub-ledgers.
- Risk management: It combines current transaction data with the previous one to detect possible fraud.
- Reporting: It gathers data from multiple sources such as computers, databases, and emails, and (as per the standard rules) it generates reports automatically.
- Payment processing: It automatically validates and reconciles pre and post-payment statements, monitors duplicate payments, notifies exceptions, and makes pending payments.
- Collections: It receives payments automatically, generates reminder reports & sends dunning letters, creates a list of customers with due payments, and allocates work to payment collectors.
RPA Can Bring Quick & Accurate Results While Being Inexpensive
Many companies are digitalizing some of their business aspects by implementing RPA, using computer-coded software bots to automate functions that humans have generally handled. Unlike AI and machine learning, RPA cannot make judgments by learning data patterns.
A bot performs actions that a human does to complete an accounting task on a computer. Bots can automate processes without requiring top-notch IT infrastructure. Bots can follow procedures that are mostly strictly prescribed, leading to solid compliance and cost-efficiency.
Compared with other accounting automation technologies, it may be inexpensive to use RPA. Adding to that cost-saving, it can deliver financial as well as non-financial benefits in less time. Many companies these days even hire outsourcing companies to get financial reporting services as most of these companies make use of RPA to help their clients improve operational efficiency and enhance business performance.
The Role of RPA’s in Financial Reporting
“According to Deloitte’s 2017 RPA survey, market trends are indicating near-universal adoption of RPA in the next five years. Average spending among companies surveyed was $1.5 million for RPA pilots and upwards of $3 million for full-scale programs.”
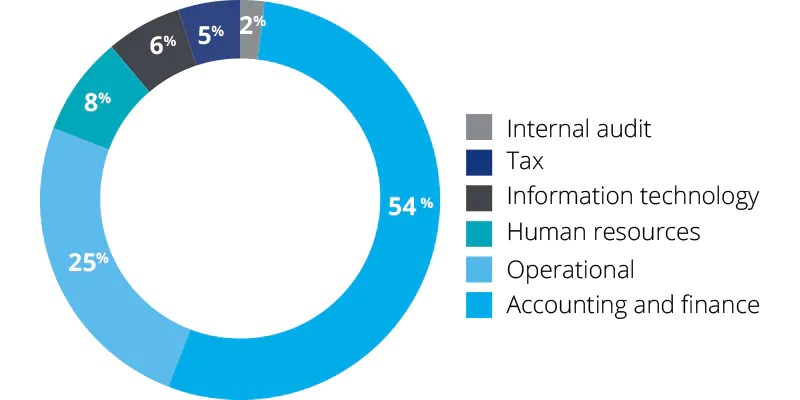
Departments that are using RPA along with their varying percentages:
- Internal audit – 2%
- Tax – 5%
- IT – 6%
- Human resources – 8%
- Operational – 25%
- Accounting & finance – 54%
Accounting and Finance is a business area that utilizes RPA more than other departments for operational improvement. The use of RPA for financial reporting services is essential because:
- The requirement of high accuracy and long-term consistency.
- It handles repetitive and manual transaction processing tasks easily.
- It does data entry & manipulation efficiently and generates accurate reports.
- Due to such characteristics, companies are automating numerous back-office operations such as accounting, including AR & AP, financial reporting & financial close.
Risks Related to the Utilization of RPA
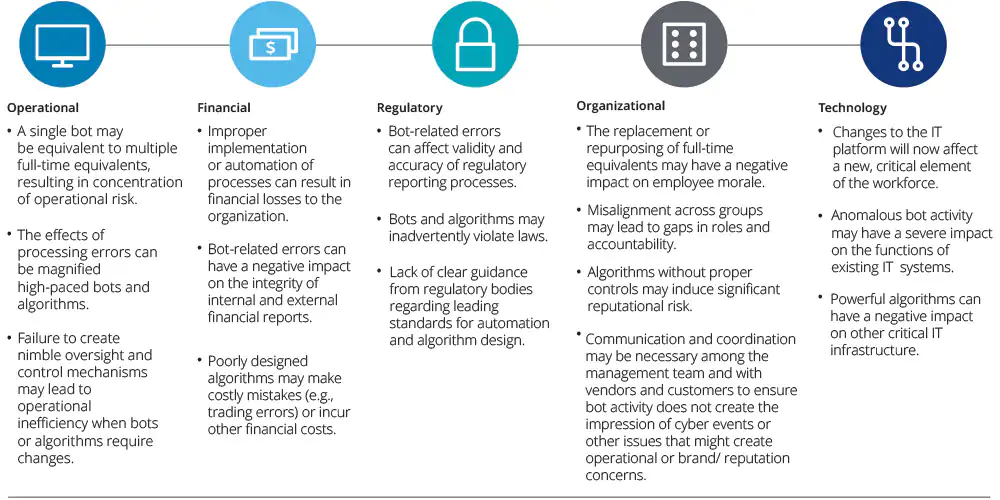
Using RPA technology for financial reporting may bring certain risks that companies need to become aware of and address. In fact, failing to identify and tackle the RPA risks properly might restrict the benefits it can actually deliver.
Companies should consider the effects of ‘improper usage of RPA’ on operations and finance, which are explained below:
- A bot that can manage the work of multiple accounting professionals is prone to OPRC – operational risk concentration.
- Failing to have complete control over RPA mechanisms might cause operational inefficiency, especially when the algorithms need to be changed.
- Improper or incomplete implementation of RPA might lead to financial loss.
- Bot-functioning errors might affect the quality of financial reports.
- Automation algorithms that are poorly designed might lead to costly errors.
Therefore, companies must have a solid governance model to keep the RPA accountable throughout its lifecycle.
How to Make Efficient Use of RPA and Prevent Potential Risks?
Companies must implement policies defining the selection, use, and development of RPA. Educating and training the employees before using RPA in any business operation is vital. For financial reporting services, you need to implement the software in the right manner:
RPA implementation phases
- Development: Developers need to perform activities to have complete control of RPA functioning, preventing risks such as the ineffective design of the bot or its becoming unable to meet the defined objective or deadline.
- Implementation: It is vital for companies to deeply consider the effects of automation on IT risk assessment and get deep insights into the IT aspects designed to support RPA-powered processes.
- Monitoring: Monitoring is the continuous process of controlling the effective use of automation in accounting processes. Moreover, monitoring and supervision programs are critical to assessing bots’ functionality.
Functions that RPA Might be Unable to Perform
Though RPA proves to be very helpful in certain cases, it is not a solution to all operational issues that often arise in a company. Tasks with which RPA might not suit:
- Complex accounting tasks such as due diligence before the acquisition, preparing and distributing investment portfolios, etc.
- The technology is unable to make significant decisions.
- Tasks that are performed annually or have an uncertain frequency.
While RPA is not the ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach for all operations, it is a brilliant tool that can make most of your financial accounting & reporting processes more productive and efficient. After considering the benefits of ARP in financial reporting, it is recommended to adopt this technology to improve the overall accounting performance of your company. However, you should also know some of the barriers that might arise while you’re on the road to RPA implementation.
Barriers to Implementing RPA for Financial Reporting
Barrier 1: Bots or Humans – A Big Dilemma
RPA is not able to make judgments by learning data patterns. Companies remain skeptical about not having humans for financial reporting services as, for them; many other steps strictly require human intervention.
Tip: Remove human interaction points that are not required and, instead, focus on the value delivered by RPA. For a limited period, have both humans and bots complete the finance and accounting processes. With this, you will have humans understand and analyze the bot’s performance to ensure the automated processes are getting completed accurately & consistently.
Barrier 2: Limited Resources
Accounting professionals often compete for resources that are already limited in their company. Though automation is proven to be helpful in financial reporting, its benefits should also be acquired by other business aspects.
Tip: Prepare an effective ROI formula and include quality-based measures apart from cost-effective measures. The objective is to obtain a comparable and accurate measure. Also, consider minimizing employee turnover, reducing rework, allocating higher-value tasks to the workforce, and improving their technological learning.
Barrier 3: Standardization Delays Implementation of Automation
Implementing any new IT system requires standardization, and many companies do the same for RPA. But, this may take a lot of time and can result in operational disruptions and delay in RPA implementation.
Tip: You can standardize financial reporting services as you start making use of RPA. This will save time and prevent the operations from getting disturbed. However, you need to be aware because, in some instances where the result will be different from the result delivered by humans, you should automate the process only after standardizing it.
Let’s now get further to some of the benefits RPA can deliver if implemented properly.
The Value Points of RPA in Finance and Accounting
RPA is capable of improving the productivity, accuracy, and accountability of the finance and accounting functions due to the following reasons:
1. It eliminates operational inconsistencies and reduces human errors.
RPA eliminates the inconsistencies that often occur due to human performance and delivers accurate outcomes consistently. “According to Gartner research, human error within the finance function produces, on average, 25,000 hours of avoidable rework at a cost of $878,000 per year.”
2. It Improves the quality of governance and control environment.
RPA can keep track of each bot’s actions, every access, everything it does, and stores all this information in a centric database for further review. The capability of the audit trail allows auditors to define accountable parties for the bot’s actions, as they can review the consistency and accuracy of the transactions and view log details to flag unauthorized or potentially risky access. It ensures seamless financial reporting services for businesses.
3. It handles repetitive work so that the workforce can focus more on higher-value business aspects.
Bots can increase productivity to the fullest, especially as compared to full-time workers, and can work 24X7 throughout the year. Most companies use RPA to manage tedious and mundane finance and accounting tasks. RPA allows companies to reduce their employees’ workload and utilize their skills and expertise for other high-value business activities.
Conclusion
To reap the most benefits from using RPA in finance and accounting, seek support from financial reporting and accounting outsourcing services providers. Human expertise combined with technology enhance operational efficiency and allow you to redeploy resources for other vital parts of your business, you must ensure the wise use of RPA. More importantly, as you now know how to control RPA implementation and utilization and risks related to this excellent technology, you can rest assured knowing that RPA-powered software will take your business ahead and not put it in jeopardy.
Examples of RPA in finance and accounting include:
- Automating vendor verification and setup processes.
- Handling purchase order entries.
- Streamlining vendor invoice processing.
- Facilitating payment preparation and execution.
- Verifying invoices against purchase orders for accuracy.
RPA can be leveraged in accounting and finance to:
- Automate the creation of balance sheets and income statements.
- Enhance financial planning and forecasting using historical data and data extracted from documents.
RPA improves financial reporting accuracy by eliminating human data entry errors, ensuring data processing consistency, and enabling real-time data validation. This reduces the likelihood of discrepancies and inaccuracies in financial reports.
RPA can lead to cost savings in financial reporting by reducing the need for manual labor, minimizing errors and associated corrections, and enabling faster report generation. This translates to lower operational costs and increased efficiency.
Latest Blogs

This site is protected by reCAPTCHA. Google's Privacy Policy
and Terms of Service apply.